chaconne is a powerful distributed job scheduling framework based on the SpringBoot framework. It can help you build a distributed task cluster easily and quickly without extra learning cost.
Chaconne Feature:
- Perfect support for SpringBoot framework (2.2.0 +)
- Support job settings in multiple ways (cron expression, parameter setting, etc.)
- Support dynamically saving jobs and deleting jobs operations
- Support configuring scheduled jobs in annotated way
- Support two scheduling methods in cluster mode (master slave mode and load balancing mode)
- Built in a variety of load balancing algorithms, supporting custom load balancing algorithms
- Support failure retry and failure over policy
- Support tracking job by logging
- Support job initial parameter with slice processing
- Support dependency of multi-jobs (serial dependency and parallel dependency)
- Support DAG to simulate business workflow
- Support customizing job termination policies
- Support job running timeout cooling and resetting
- Support email alarm for job failure
Two deployment mode of Chaconne Application Cluster:
- Decentralized deployment mode
- No fixed scheduling center role, the chaconne cluster will elect one of the applications as a leader for job scheduling
- Applications participating in scheduling and execution interact through TCP protocol
- Centralized deployment mode
- It is divided into two roles: scheduling center and job executor, and both scheduling center and job executor support cluster mode
- The scheduling center interacts with the job executor through HTTP protocol
Description: The cluster here refers to the cluster composed of applications participating in job execution (chaconne cluster). It is an independent concept from the cluster composed of SpringCloud framework
If the chaconne cluster is small, the decentralized deployment mode is recommended. If the cluster is large, both modes can be used according to the actual situation.
Structure of the Chaconne Framework:
- chaconne-spring-boot-starter
The core jar of chaconne, which contains all the core functions of chaconne (including the external API of the Web UI) - chaconne-console Chaconne Web UI,Doing job management and query job running status
- chaconne-manager If centralized deployment is adopted, you can refer this demo of scheduling center
Install:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.paganini2008.atlantis</groupId>
<artifactId>chaconne-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-RC3</version>
</dependency>
(Please use the latest version)
Compatibility:
- Jdk1.8 (or later)
- SpringBoot 2.2.0 (or later)
- Redis 3.0 (or later)
- MySQL 5.0 (or later)
Description:
- Redis is used to access cluster information and broadcast messages
- MySQL is used to save job definition and runtime related data. At present, it only supports MySQL. Relevant Tables will be created automatically when the application starts
Required Settings:
spring.application.cluster.name=jobtester-cluster # set chaconne cluster name
spring.application.name=jobtester
#Jdbc Configuration
atlantis.framework.chaconne.datasource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?userUnicode=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=UTF8&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull
atlantis.framework.chaconne.datasource.username=fengy
atlantis.framework.chaconne.datasource.password=123456
atlantis.framework.chaconne.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#Redis Configuration
atlantis.framework.redis.host=localhost
atlantis.framework.redis.port=6379
atlantis.framework.redis.password=123456
atlantis.framework.redis.database=0
spring.redis.messager.pubsub.channel=chaconne-management-messager-pubsub
Brief introduction of chaconne implementation principle
The bottom layer of chaconne relies on the tridenter-spring-boot-starter component to realize the task cluster mode (active standby mode and load balancing mode), and uses the message unicast mechanism (simulated by Redis PubSub) to realize task distribution, load balancing, fragment processing and other advanced features. Note that the definition of cluster in chaconne framework is consistent with that in tridenter-spring-boot-starter. The concept of cluster is equivalent to distinguishing different product groups or companies. At the same time, chaconne also supports the concept of task group, which is an optional configuration. By default, the group name is the current application name (${spring. Application. Name}), If there are multiple applications with the same application name, these applications become a task group. Chaconne supports not only cross group task calls, but also cross cluster task calls.
How to define a Job?
- Using annotation
@ChacJob - Inherit
ManagedJob - Implements
Job - Implements
NotManagedJob
Description:
- The first three methods of defining Job belong to declarative (programming) definition, In other word, a task is defined in code and loaded automatically with the start of the Spring Framework context
- The last definition method is used to define dynamic tasks. Users can submit to create jobs on the Web UI (Chaconne Console) or directly create tasks by calling HTTP API / SDK. Note that the job objects created by this way do not belong to bean objects managed by Spring Application Context
Examples:
- Creating a Job by annotation
@ChacJob
@ChacTrigger(cron = "*/5 * * * * ?")
public class DemoCronJob {
@Run
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) throws Exception {
log.info("DemoCronJob is running at: {}", DateUtils.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
return RandomUtils.randomLong(1000000L, 1000000000L);
}
@OnSuccess
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
log.info("DemoCronJob's return value is: {}", result);
}
@OnFailure
public void onFailure(JobKey jobKey, Throwable e, Logger log) {
log.error("DemoCronJob is failed by cause: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
- Creating a Job by implementing
Job
@Component
public class HelloWorldJob implements Job {
@Override
public String getClusterName() {
return "your_cluster_name";
}
@Override
public String getGroupName() {
return "your_group_name";
}
@Override
public int getRetries() {
return 3;
}
@Override
public long getTimeout() {
return 60 * 1000L;
}
@Override
public String getEmail() {
return "your_email@helloworld.com";
}
@Override
public Trigger getTrigger() {
return GenericTrigger.Builder.newTrigger(1L, SchedulingUnit.MINUTES, false).build();
}
@Override
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger logger) {
return "Hello World!";
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(result.toString());
}
}
}
- Creating a Job by inherit
ManagedJob
@Component
public class HealthCheckJob extends ManagedJob {
@Override
public long getTimeout() {
return 60L * 1000;
}
@Override
public Trigger getTrigger() {
return GenericTrigger.Builder.newTrigger("*/5 * * * * ?").setStartDate(DateUtils.addSeconds(new Date(), 30)).build();
}
@Override
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object arg, Logger log) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(info());
}
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(result.toString());
}
}
private String info() {
long totalMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory();
long usedMemory = totalMemory - Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory();
return FileUtils.formatSize(usedMemory) + "/" + FileUtils.formatSize(totalMemory);
}
}
How to create a dynamic task?
-
Create on the Web UI (Described Later)
-
Create by API
- Creating a Job by inherit
NotManagedJob``` java public class EtlJob implements NotManagedJob {
@Override public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) { log.info(“JobKey:{}, Parameter: {}”, jobKey, attachment); return null; }
- Creating a Job by inherit
}
* Using HTTP API
POST http://localhost:6543/job/admin/persistJob
``` json
{
"jobKey": {
"clusterName": "yourCluster",
"groupName": "yourGroup",
"jobName": "yourJob",
"jobClassName": "com.yourcompany.yourapp.YourJob"
},
"description": "Describe your job shortly",
"email": "YourEmail@yourcompany.com",
"retries": 0,
"timeout": -1,
"weight": 100,
"dependentKeys": null,
"forkKeys": null,
"completionRate": -1,
"trigger": {
"triggerType": 1,
"triggerDescription": {
"cron": {
"expression": "*/5 * * * * ?"
}
},
"startDate": null,
"endDate": null,
"repeatCount": -1
},
"attachment": "{\"initialParameter\": \"test\"}"
}
- Using SDK
@Component
public class TestService {
@Autowired
private JobManager jobManager;
public void createJob() throws Exception {
final JobKey jobKey = JobKey.by("yourCluster", "yourGroup", "yourJob", "com.yourcompany.yourapp.YourJob");
GenericJobDefinition.Builder builder = GenericJobDefinition.newJob(jobKey)
.setDescription("Describe your job shortly")
.setEmail("YourEmail@yourcompany.com")
.setRetries(3)
.setTimeout(60000L);
GenericTrigger.Builder triggerBuilder = GenericTrigger.Builder.newTrigger("*/5 * * * * ?");
builder.setTrigger(triggerBuilder.build());
GenericJobDefinition jobDefinition = builder.build();
jobManager.persistJob(jobDefinition, "{\"initialParameter\": \"test\"}");
}
}
Note: It is recommended that the job initializing parameter is in JSON format.
Job dependency
Job dependency is one of the important features of Chaconne Framework. Job dependency can be divided into Serial Dependency and Parallel Dependency. Serial dependency means that Job A is completed and then Job B will be executed, We can see Job B depends on Job A. So what does parallel dependency? For example, there are three tasks, Job A, Job B, and Job C. Job C can only be executed after Job A and Job B are all completed, which is similar to countersignature. Both serial dependency and parallel dependency can share job initializing parameters and running results during the job execution, and support user-defined judgment strategies to decide whether to trigger downstream tasks.
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
Based on the combination of serial dependency and parallel dependency, Chaconne Framework provides DAG function and friendly API to simulate business scenarios similar to workflow, which enriches the use scenarios of task dependency. (for the convenience of examples, tasks are configured by annotation)
- Serial Dependency
@ChacJob
@ChacTrigger(triggerType = TriggerType.DEPENDENT)
@ChacDependency({ @ChacJobKey(className = "com.chinapex.test.chaconne.job.DemoSchedJob", name = "demoSchedJob") })
public class DemoDependentJob {
@Run
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) throws Exception {
log.info("DemoDependentJob is running at: {}", DateUtils.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
return RandomUtils.randomLong(1000000L, 1000000000L);
}
@OnSuccess
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
log.info("DemoDependentJob's return value is: {}", result);
}
@OnFailure
public void onFailure(JobKey jobKey, Throwable e, Logger log) {
log.error("DemoDependentJob is failed by cause: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
- Parallel dependency:
Here are three Jobs,
DemoTask,DemoTaskOne,DemoTaskTwo
Let DemoTaskOne and DemoTaskTwo finish before executing DemoTask, and DemoTask can get the result data of DemoTaskOne and DemoTaskTwo after execution
DemoTaskOne.java
@ChacJob
@ChacTrigger(triggerType = TriggerType.SIMPLE)
public class DemoTaskOne {
@Run
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) throws Exception {
log.info("DemoTaskOne is running at: {}", DateUtils.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
return RandomUtils.randomLong(1000000L, 1000000000L);
}
@OnSuccess
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
log.info("DemoTaskOne return value is: {}", result);
}
@OnFailure
public void onFailure(JobKey jobKey, Throwable e, Logger log) {
log.error("DemoTaskOne is failed by cause: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
DemoTaskTwo.java
@ChacJob
@ChacTrigger(triggerType = TriggerType.SIMPLE)
public class DemoTaskTwo {
@Run
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) throws Exception {
log.info("DemoTaskTwo is running at: {}", DateUtils.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
return RandomUtils.randomLong(1000000L, 1000000000L);
}
@OnSuccess
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
log.info("DemoTaskTwo return value is: {}", result);
}
@OnFailure
public void onFailure(JobKey jobKey, Throwable e, Logger log) {
log.error("DemoTaskTwo is failed by cause: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
DemoTask.java
@ChacJob
@ChacTrigger(cron = "0 0/1 * * * ?", triggerType = TriggerType.CRON)
@ChacFork({ @ChacJobKey(className = "com.chinapex.test.chaconne.job.DemoTaskOne", name = "demoTaskOne"),
@ChacJobKey(className = "com.chinapex.test.chaconne.job.DemoTaskTwo", name = "demoTaskTwo") })
public class DemoTask {
@Run
public Object execute(JobKey jobKey, Object attachment, Logger log) throws Exception {
log.info("DemoTask is running at: {}", DateUtils.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
TaskJoinResult joinResult = (TaskJoinResult) attachment;
TaskForkResult[] forkResults = joinResult.getTaskForkResults();
long max = 0;
for (TaskForkResult forkResult : forkResults) {
max = Long.max(max, (Long) forkResult.getResult());
}
return max;
}
@OnSuccess
public void onSuccess(JobKey jobKey, Object result, Logger log) {
log.info("DemoTask return max value is: {}", result);
}
@OnFailure
public void onFailure(JobKey jobKey, Throwable e, Logger log) {
log.error("DemoTask is failed by cause: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
- Create a DAG Dag Jobs only support API creation at present
@RequestMapping("/dag")
@RestController
public class DagJobController {
@Value("${spring.application.cluster.name}")
private String clusterName;
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String applicationName;
@Autowired
private JobManager jobManager;
@GetMapping("/create")
public Map<String, Object> createDagTask() throws Exception {
Dag dag = new Dag(clusterName, applicationName, "testDag");
dag.setTrigger(new CronTrigger("0 0/1 * * * ?"));
dag.setDescription("This is only a demo of dag job");
DagFlow first = dag.startWith(clusterName, applicationName, "demoDagStart", DemoDagStart.class.getName());
DagFlow second = first.flow(clusterName, applicationName, "demoDag", DemoDag.class.getName());
second.fork(clusterName, applicationName, "demoDagOne", DemoDagOne.class.getName());
second.fork(clusterName, applicationName, "demoDagTwo", DemoDagTwo.class.getName());
jobManager.persistJob(dag, "123");
return Collections.singletonMap("ok", 1);
}
}
The above DAG example illustrates that the DAG model provided by the chaconne framework supports serial inflow, that is, flow mode, and also provides fork mode for parallel processing. In the above example, the task demoDag forks two sub-processes (“demoDagOne” and “demoDagTwo” ), that is, demoDagOne and demoDagTwo are processed at the same time and then the demoDag task is triggered.
Deployment description
- Decentralized deployment
Add the
@EnableChaconneEmbeddedModeannotation to the main function of your spring application, and then start your application. Example:
@EnableChaconneEmbeddedMode
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan
public class YourApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int port = 8088;
System.setProperty("server.port", String.valueOf(port));
SpringApplication.run(YourApplicationMain.class, args);
}
}
- Centralized deployment
- To start the scheduling center, you need to create a new SpringBoot project, add annotation
@EnableChaconneDetachedModeto the main function and specify it as the production side Example:
- To start the scheduling center, you need to create a new SpringBoot project, add annotation
@EnableChaconneDetachedMode(DetachedMode.PRODUCER)
@SpringBootApplication
public class ChaconneManagementMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ChaconneManagementMain.class, args);
}
}
(DataSource and RedisConnectionFactory need to be configured)
Or use the annotation @ChaconneAdmin directly
Example:
@ChaconneAdmin
@SpringBootApplication
public class ChaconneManagerApplication {
static {
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled", "false");
File logDir = FileUtils.getFile(FileUtils.getUserDirectory(), "logs", "indi", "atlantis", "framework", "chaconne", "management");
if (!logDir.exists()) {
logDir.mkdirs();
}
System.setProperty("LOG_BASE", logDir.getAbsolutePath());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ChaconneManagerApplication.class, args);
System.out.println(Env.getPid());
}
}
- Add the
@EnableChaconneDetachedModeannotation to the main function of your Spring application (the default is the consumer side), and then start
@EnableChaconneDetachedMode
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan
public class YourApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int port = 8088;
System.setProperty("server.port", String.valueOf(port));
SpringApplication.run(YourApplicationMain.class, args);
}
}
How to use Chaconne Console?
Chaconne Console is a Web project for task management and viewing provided by the chaconne framework. It also supports decentralized deployment and centralized deployment mode. The default port is 6140
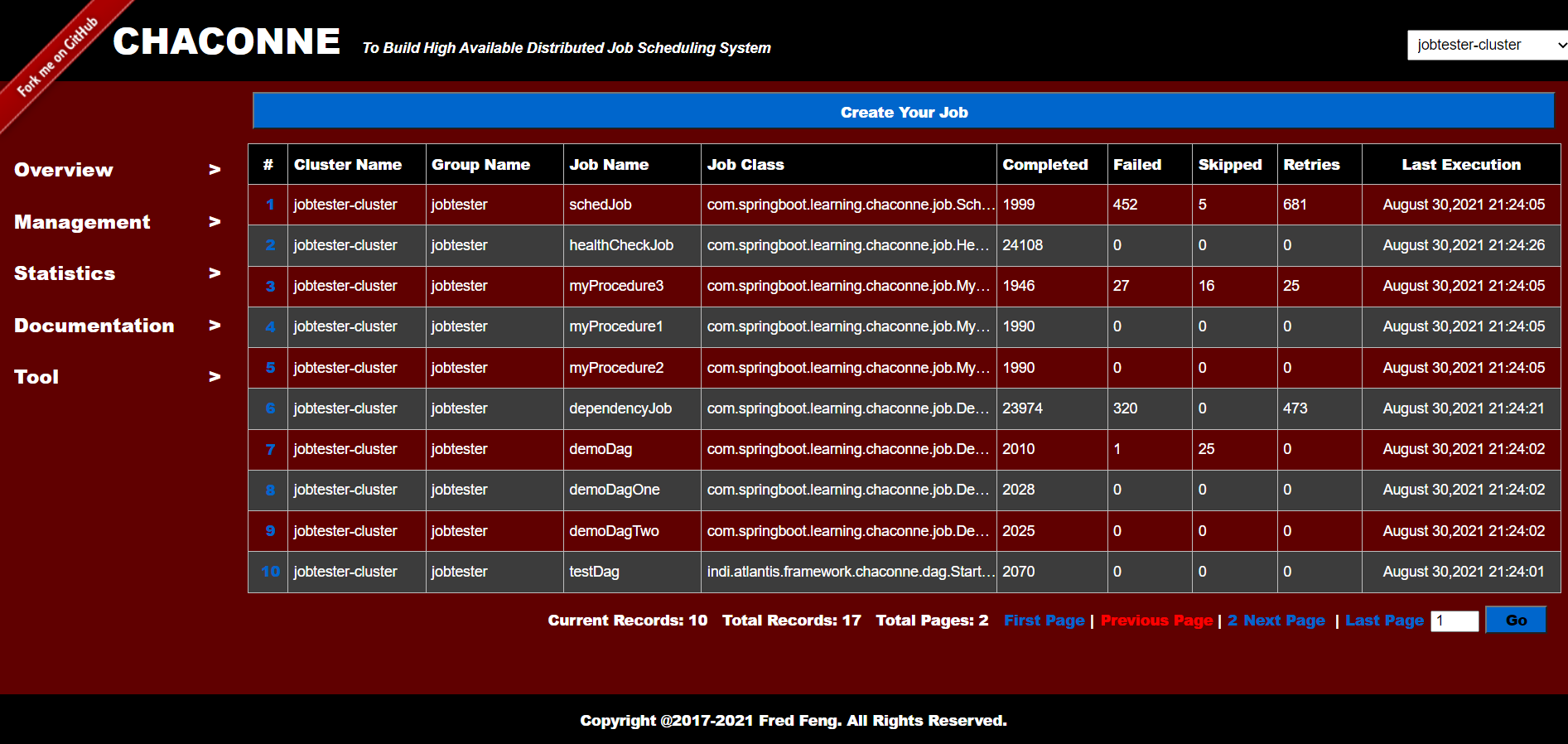
Provides the following functions:
- Save tasks and view task information
- Pause and resume tasks
- Delete task
- Run the task manually
- View task statistics (by day)
- View task runtime log
At present, the Chaconne Console project is still under continuous maintenance. Some functions are slightly rough, and some functions are not yet open. Similarly, Chaconne Console is also a SpringBoot project Source Code:
@EnableChaconneClientMode
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })
public class ChaconneConsoleMain {
static {
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled", "false");
File logDir = FileUtils.getFile(FileUtils.getUserDirectory(), "logs", "indi", "atlantis", "framework", "chaconne", "console");
if (!logDir.exists()) {
logDir.mkdirs();
}
System.setProperty("DEFAULT_LOG_BASE", logDir.getAbsolutePath());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ChaconneConsoleMain.class, args);
System.out.println(Env.getPid());
}
}
The annotation @EnableChaconneClientMode means to enable a task management client
After startup, enter the homepage address: http://localhost:6140/chaconne/index
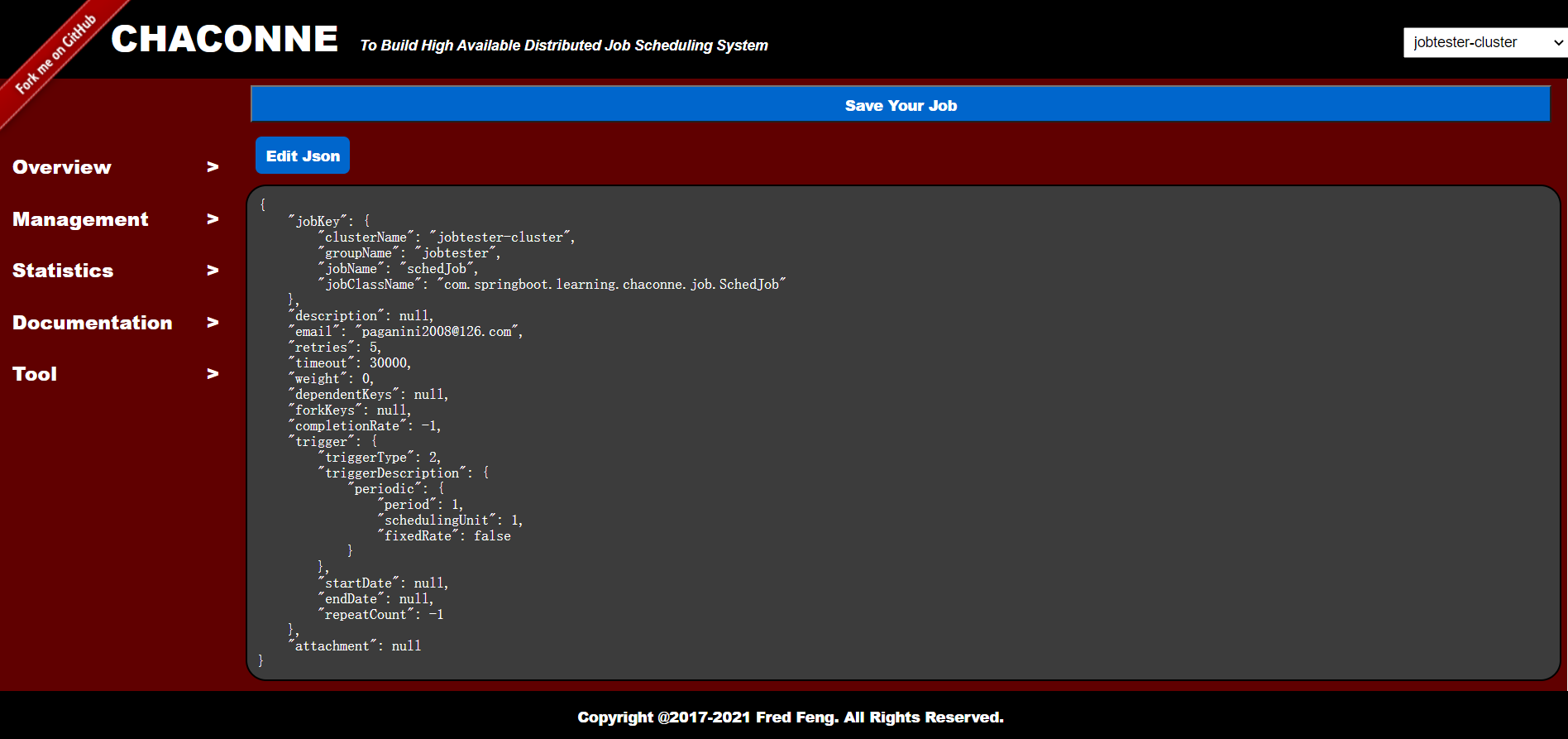
You will see:
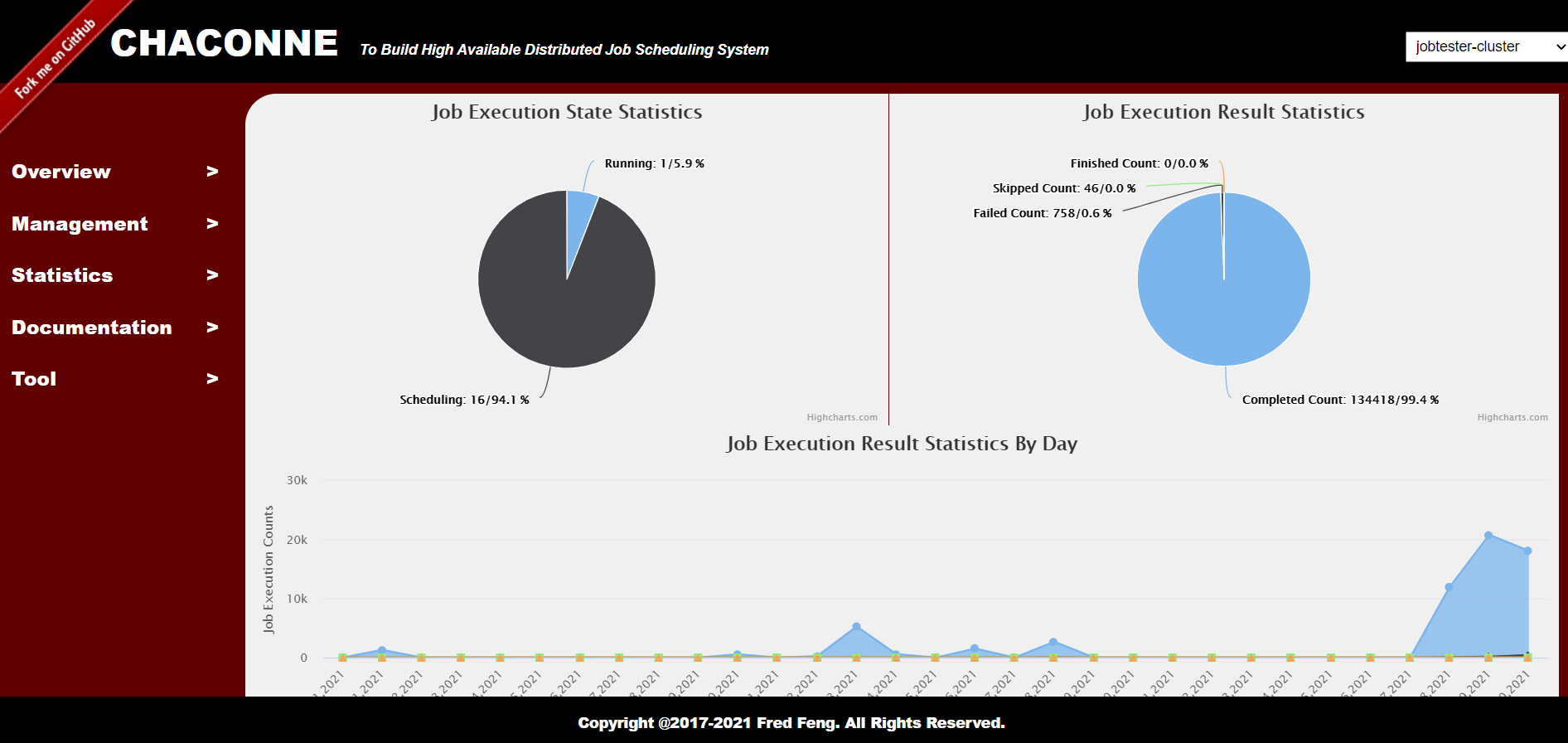
Job List:
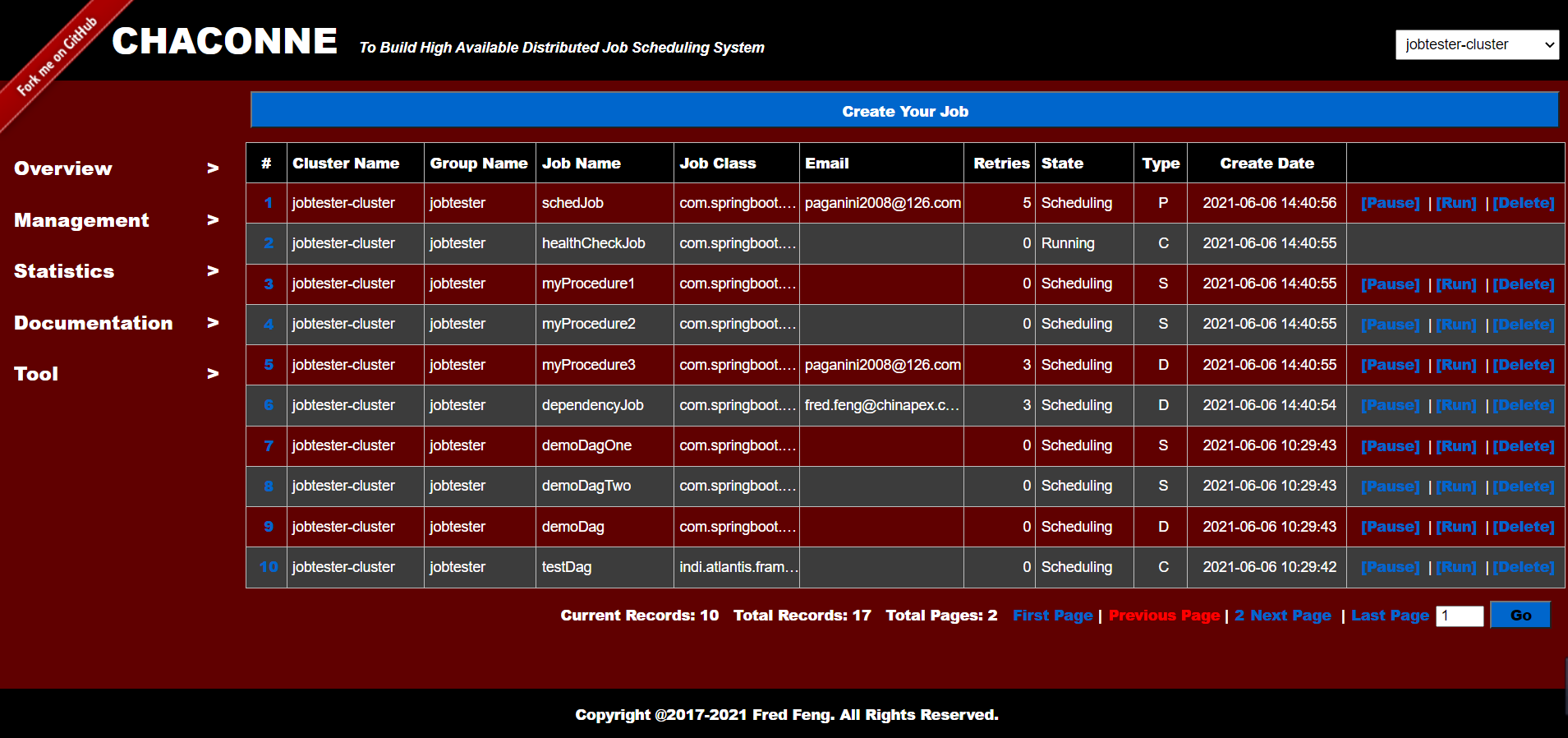
Create a Job:
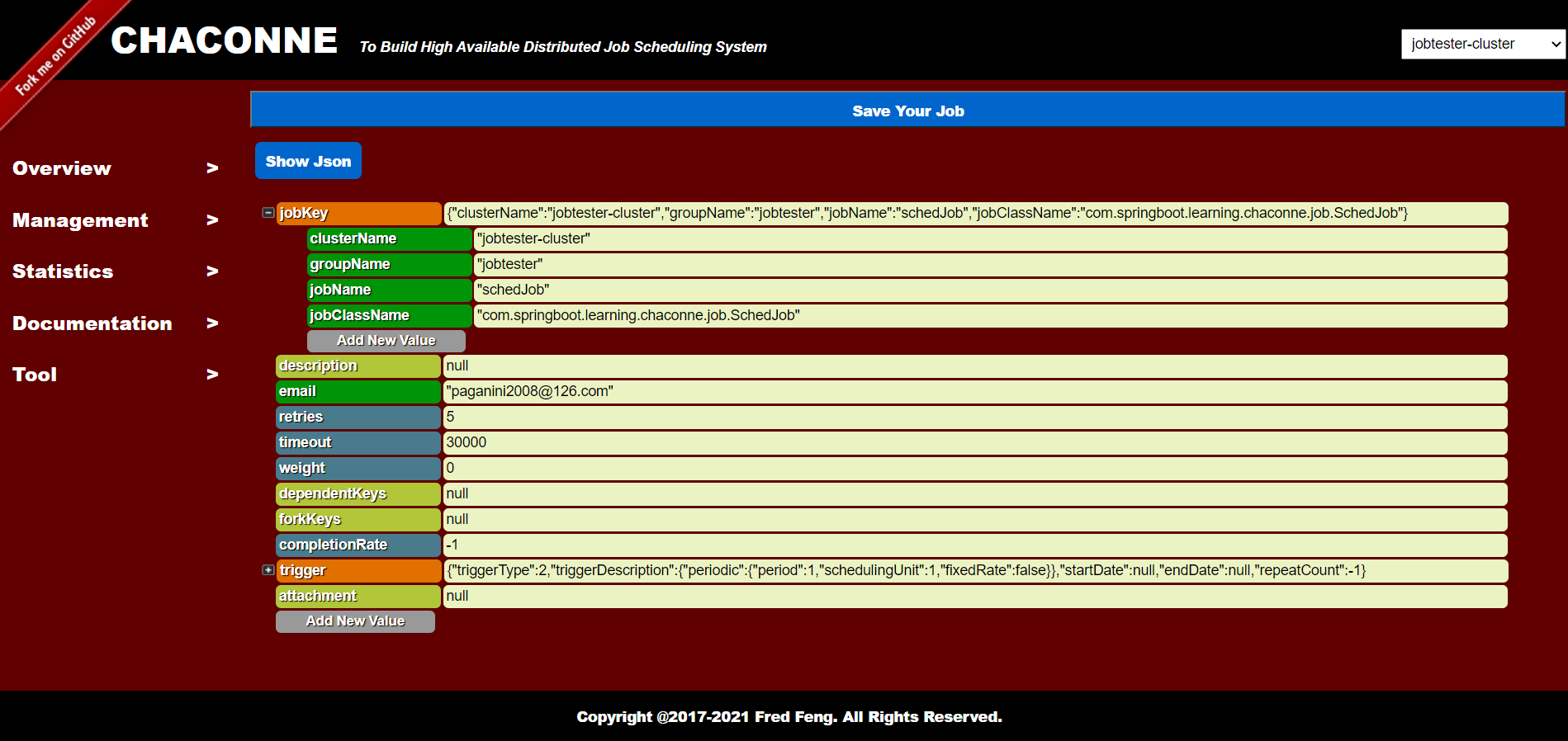
Job Json Data:
Job Detail:
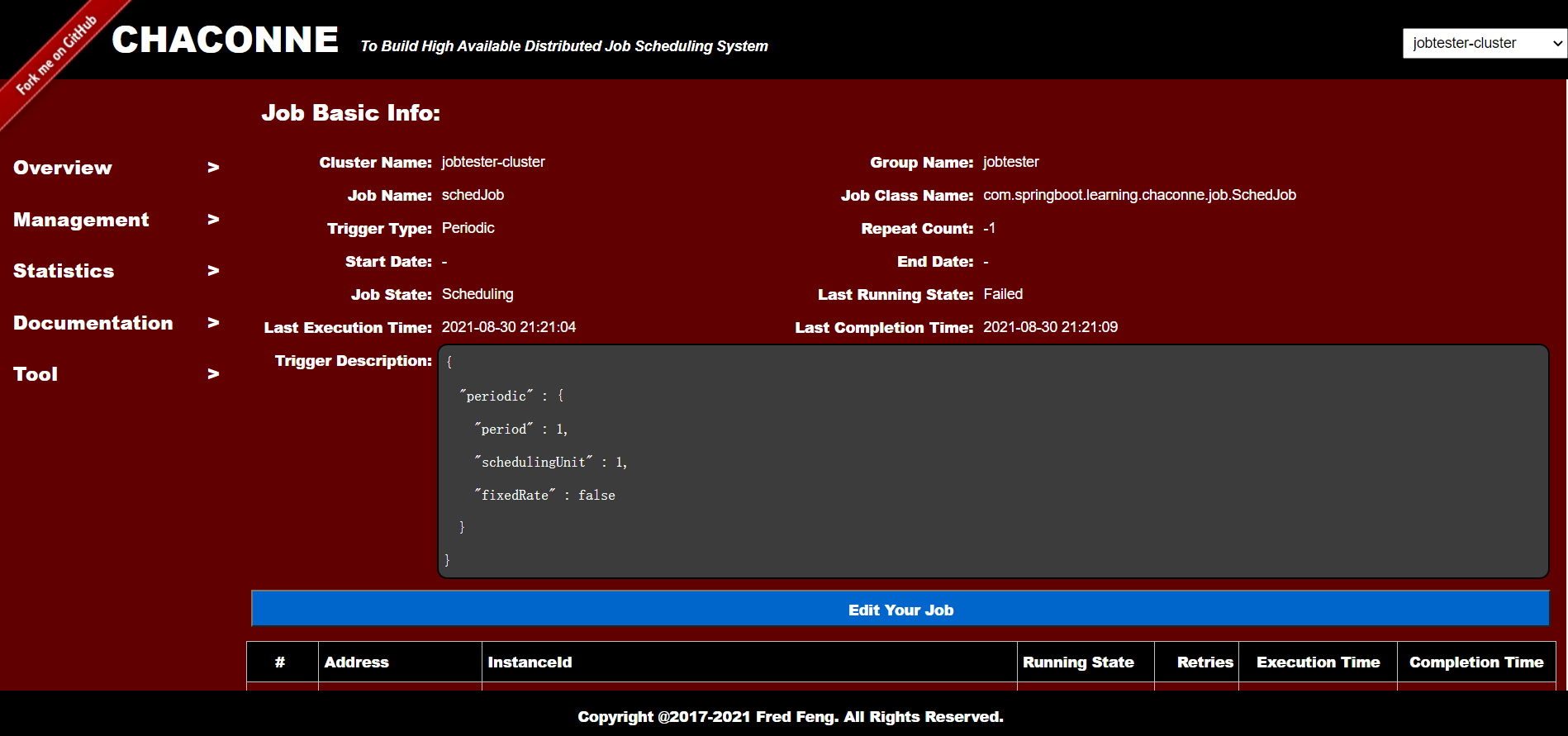
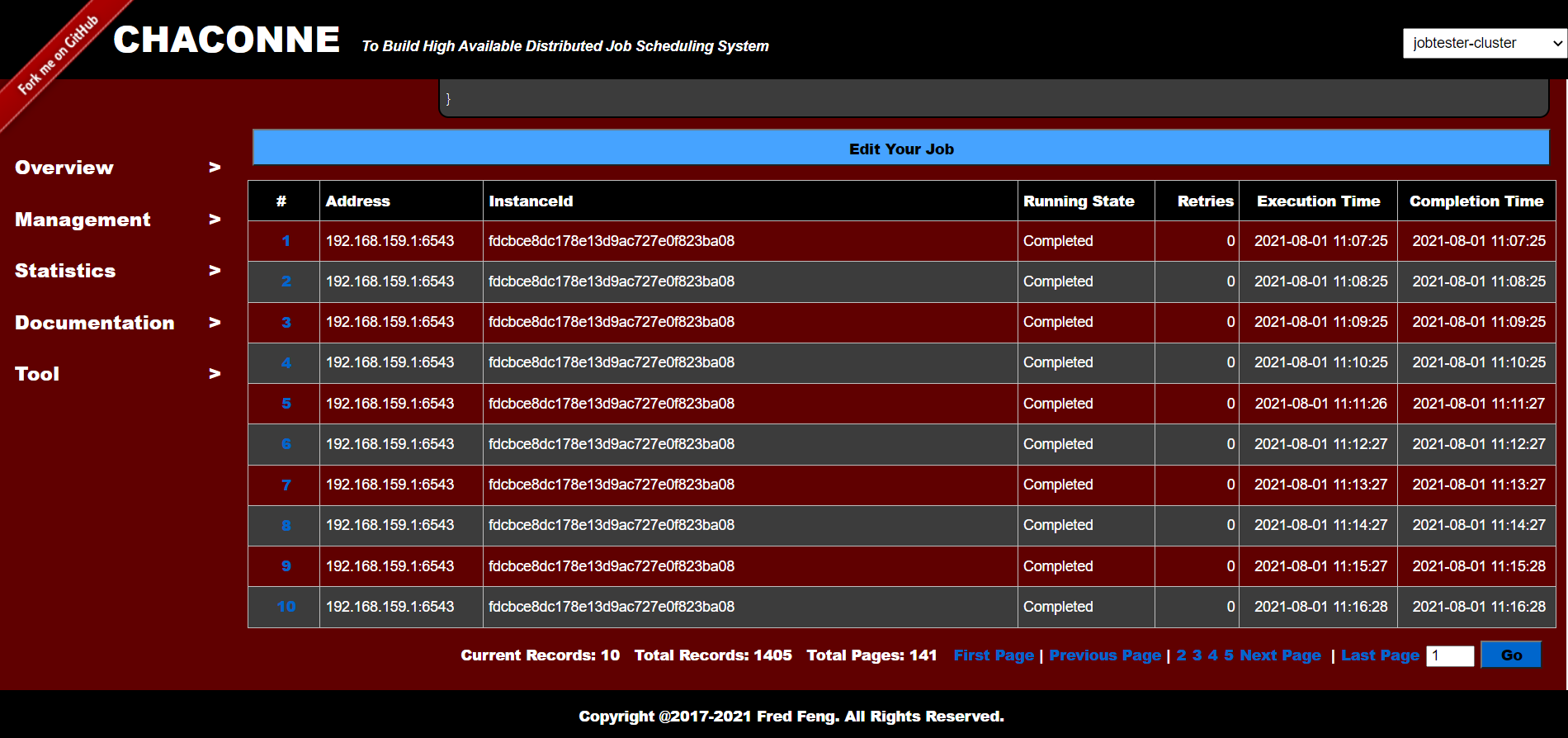
Job Trace:
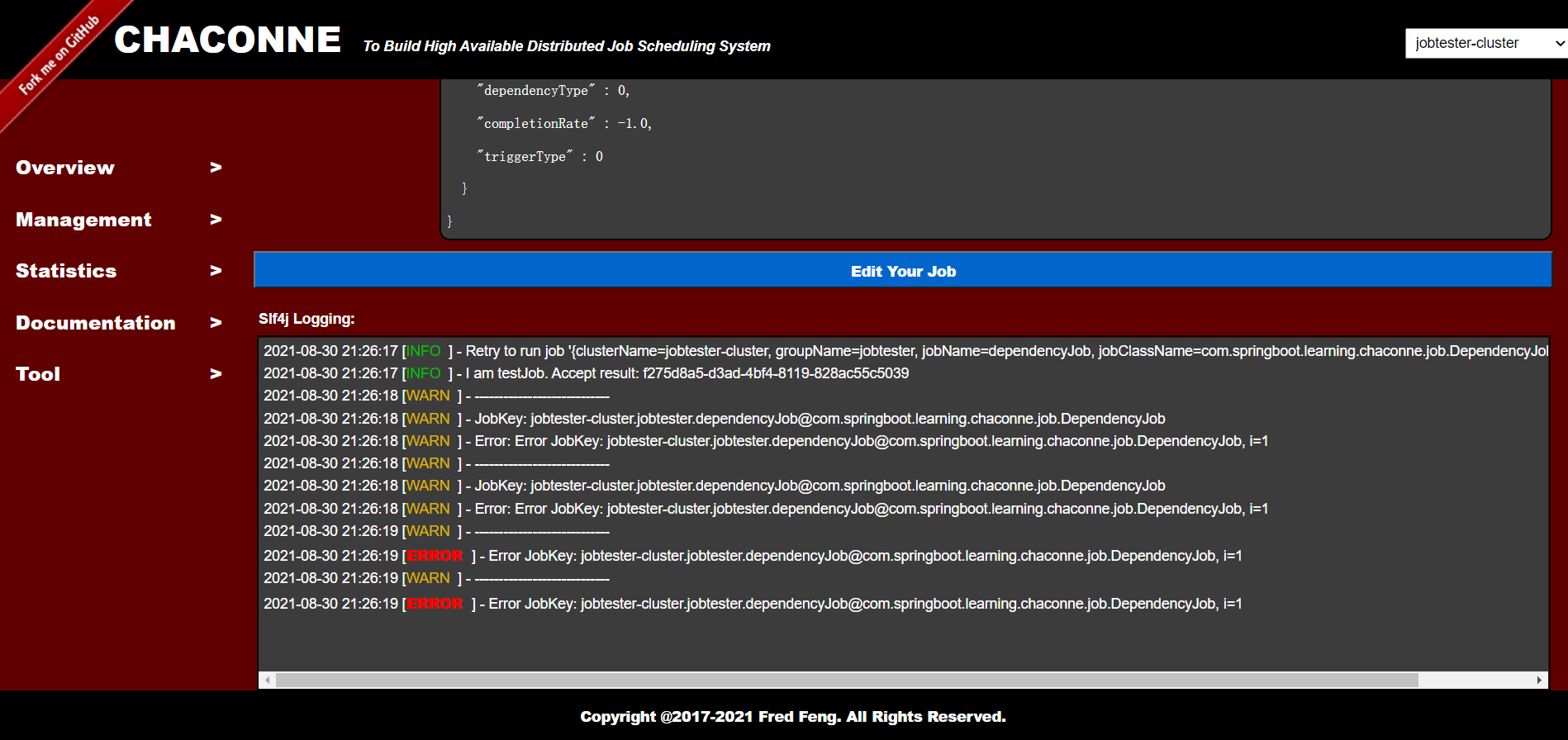
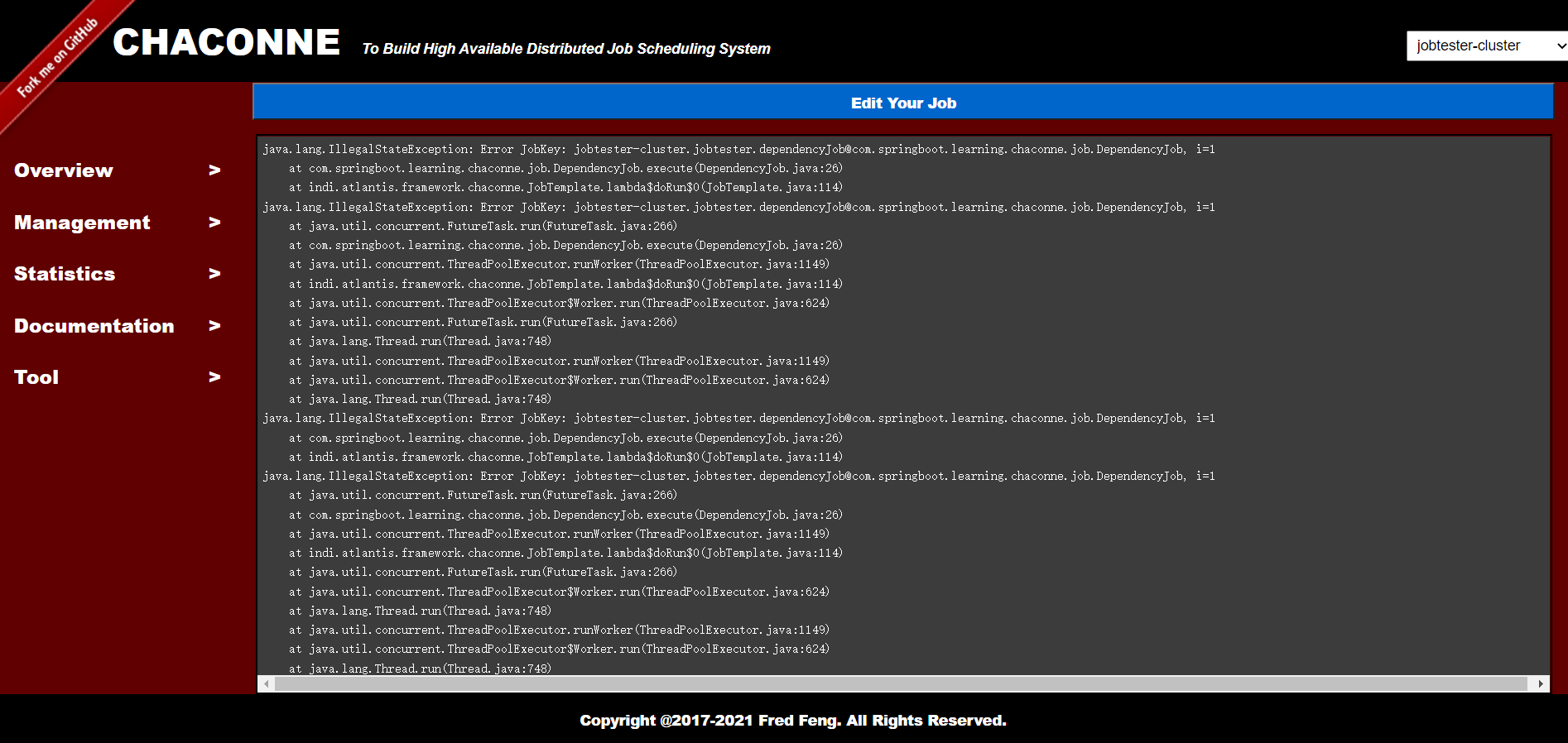
Job Log:
-
info:
-
error:
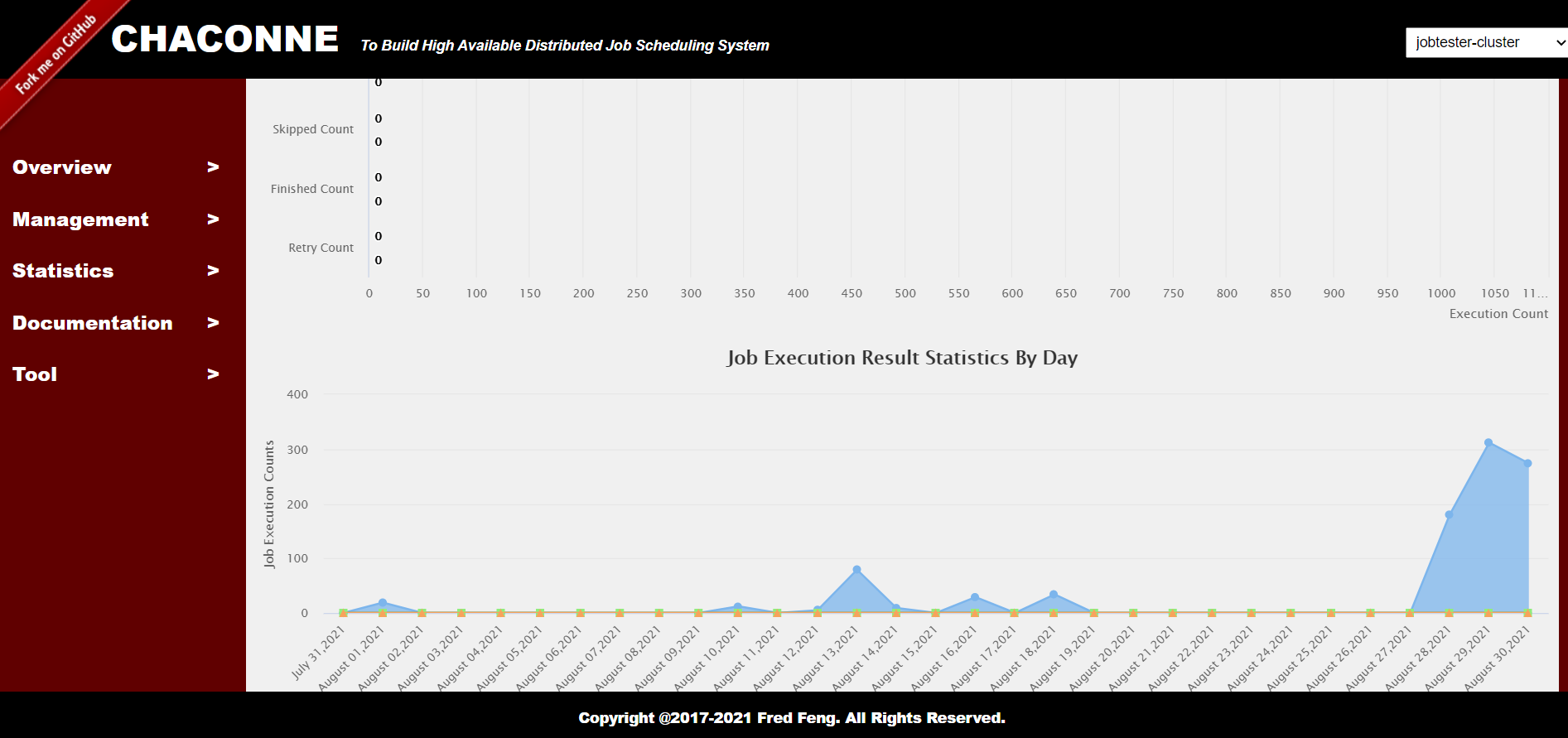
Job Statistics:
 You can view the statistics of each job (by day)
You can view the statistics of each job (by day)
Documentation:
Git repository:https://github.com/paganini2008/chaconne.git